How to make ViewState secure in ASP.NET
By , 26 Jan 2011
|
Introduction
The ASP.NET ViewState is a client side state management mechanism. The ViewState is stored in a hidden field with an ID__VIEWSTATE. Typically, stored ViewState information looks like: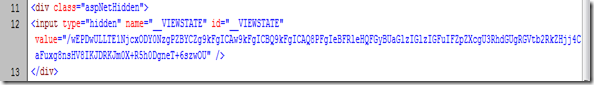
Now let us look at the value. It looks likes an encrypted string. This is nothing but a Base64 encoded string, and is not an encrypted string. So it can be easily decoded.
The main reasons for using Base64 encoding are as follows:
- Base64 makes a string suitable for HTTP transfers
- It makes it a little harder to read
Let us try to decode the string using ViewState Decoder (a nice tool created by Fritz Onion).
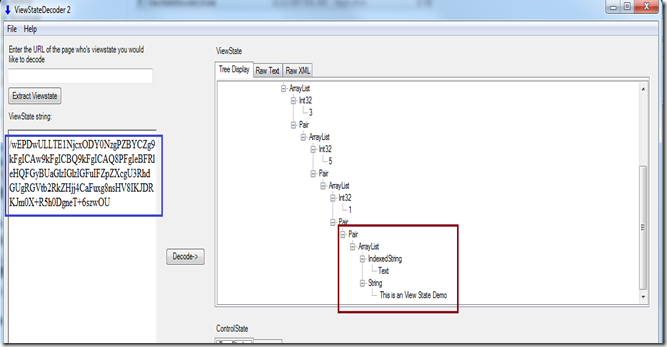
After decoding the string, we can see the exact data that is stored inside the ViewState.
You can write a few lines of code to decode the text and you will get the actual View State information.
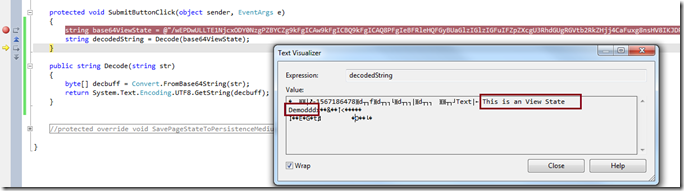
So here is how the ViewState works:
By default, ViewState is serialized into a Base-64 encoded string. On postback, the ViewState information is loaded and reapplied to the persisted state of the control in the control hierarchy.
Solution
There are two different ways in which you can prevent someone from decrypting ViewState data.- You can make sure that the ViewState information is tamper-proof by using "hash codes". You can do this by adding
EnableViewStateMAC=truein your page directive. MAC stands for "Message Authentication Code". - The second option is to set
ViewStateEncryptionMode="Always"with your page directives. This will encrypt the ViewState data. You can do this like:

When we use
EnableViewStateMac="True", during ViewState save, ASP.NET internally uses a hash code. This hash code is a cryptographically strong checksum. This is added with the ViewState content and stored in a hidden filed. During postback, the checksum data is verified again by ASP.NET. If there is a mismatch, the postback will be rejected.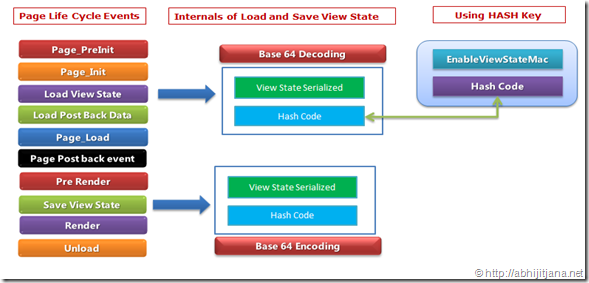

ViewStateEncryptionMode has three different options that can be set:Always: encrypt the View State always.Auto: encrypt if a control requests for encryption. For this to happen, the control must call thePage.RegisterRequiresViewStateEncryption()method.Never: Never encrypt the ViewState.
ViewStateEncryptionMode="Always" and try to decode ViewState data, you will get information as shown below:
We can also enable these settings for
EnableViewStateMAC and ViewStateEncryptionMode in web.config:
Note: Try to avoid ViewState encryption if it is not necessary as it can cause performance issues.
If you are a beginner to ViewState, please read my article on ViewState – Beginner’s Guide to View State.


Comments
Post a Comment